Mold in Garage: Complete Removal & Prevention Guide
Expert solutions to identify, remove, and prevent garage mold growth
Garages are among the most overlooked areas when it comes to home maintenance, yet they’re highly susceptible to mold growth. Whether you have an attached or detached garage, moisture from vehicles, poor ventilation, and temperature fluctuations create ideal conditions for mold colonization. By the time most homeowners notice the problem, mold has already established itself on ceilings, walls, concrete floors, or stored items.
Understanding how to identify, remove, and prevent garage mold protects your health, preserves your property value, and ensures your garage remains a functional space. This comprehensive guide draws on our experience from over 15,000 mold inspections across Ontario and Quebec to help you address garage mold effectively.
⚠️ Concerned About Mold in Your Garage? Get a Free Inspection!
Garages are often neglected spots where mold can thrive. Don’t let mold go unchecked! Contact Mold Busters for a free virtual mold inspection. Our experts will provide a thorough assessment and a plan to eliminate any mold issues, ensuring your garage is safe. Act now to protect your space!
How to Tell If You Have Mold in Your Garage: Warning Signs
Early detection is key: Look for visual signs (black, white, or green patches), musty odors, and health symptoms that worsen when spending time in your garage.
Early detection of garage mold prevents extensive damage and health complications. Many homeowners miss early warning signs because they don’t spend significant time in their garage or mistake mold for dirt or stains. Recognizing these indicators helps you act before the problem escalates.
Visual Signs of Mold Growth
🖤 Black Mold Indicators
- Dark greenish-black patches
- Slimy texture on surfaces
- Found on drywall, wood, or ceilings
⚪ White Mold Signs
- Powdery, cotton-like appearance
- Often on concrete surfaces
- Can be mistaken for mineral deposits
💚 Green Mold Appearance
- Olive-green to brown coloring
- Fuzzy or velvety texture
- Found on various materials
Look for discoloration on garage ceilings near roof joints, dark spots on drywall behind stored items, fuzzy growth on concrete floors near drainage areas, and patches on the interior panels of garage doors. Black spots on garage ceiling materials often indicate moisture problems from roof leaks or condensation.
Musty Smell and Odor Detection
A persistent musty, earthy smell in your garage signals mold growth even when you can’t see visible colonies. This distinctive mold smell results from microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) that mold releases as it grows. The odor intensifies in humid weather or when the garage has been closed for extended periods.
💡 Detection Tip: If your garage smells musty after rain or when temperatures fluctuate, investigate behind stored items, check ceiling corners, and examine areas around the garage door seal.
Physical Symptoms in Garage Users
Regular garage users may experience health symptoms that worsen when spending time in the space. Common indicators include persistent coughing or throat irritation when working in the garage, headaches that develop during garage activities, eye irritation or watery eyes, and respiratory discomfort or asthma aggravation. If you notice these symptoms improve when you leave the garage, mold exposure may be the cause.
Is Mold in a Garage Dangerous to Your Health?
⚠️ Health Warning
All molds pose potential health risks through allergic reactions, respiratory irritation, and toxic effects from mycotoxin exposure in certain species.
Mold in any indoor environment poses health risks, though severity varies based on exposure duration, mold type, and individual sensitivity. Understanding these risks helps you determine appropriate urgency for remediation.
All molds have the potential to cause health problems through three primary mechanisms: allergic reactions from immune system responses, respiratory irritation from spore inhalation, and toxic effects from mycotoxin exposure in certain species. Even non-toxic molds trigger allergic responses in sensitive individuals.
Health Risks by Population
👶 Children & Infants
- Developing respiratory systems
- Higher breathing rates per body weight
- Risk of respiratory infections
- Asthma condition exacerbation
🏥 Compromised Immune Systems
- Chemotherapy patients
- HIV/AIDS individuals
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Serious infection risks
🫁 Respiratory Conditions
- Asthma sufferers
- COPD patients
- Chronic bronchitis
- Symptom aggravation
🐾 Pets
- Respiratory distress
- Skin irritation
- Digestive issues
- Lethargy and appetite loss
Black Mold Concerns in Garages
Stachybotrys chartarum, commonly called “black mold” or “toxic black mold,” produces mycotoxins that can cause severe health effects including chronic fatigue, persistent headaches, respiratory disorders, memory problems, and in extreme cases, bleeding in the lungs. However, not all black-colored mold is Stachybotrys—proper identification through professional testing determines actual risk levels.
🚨 Important: If you suspect black mold on your garage ceiling, walls, or other surfaces, avoid disturbing it through attempted DIY cleaning. Disturbance releases massive spore quantities into the air, increasing exposure risk. Contact professional mold remediation services for safe assessment and removal.
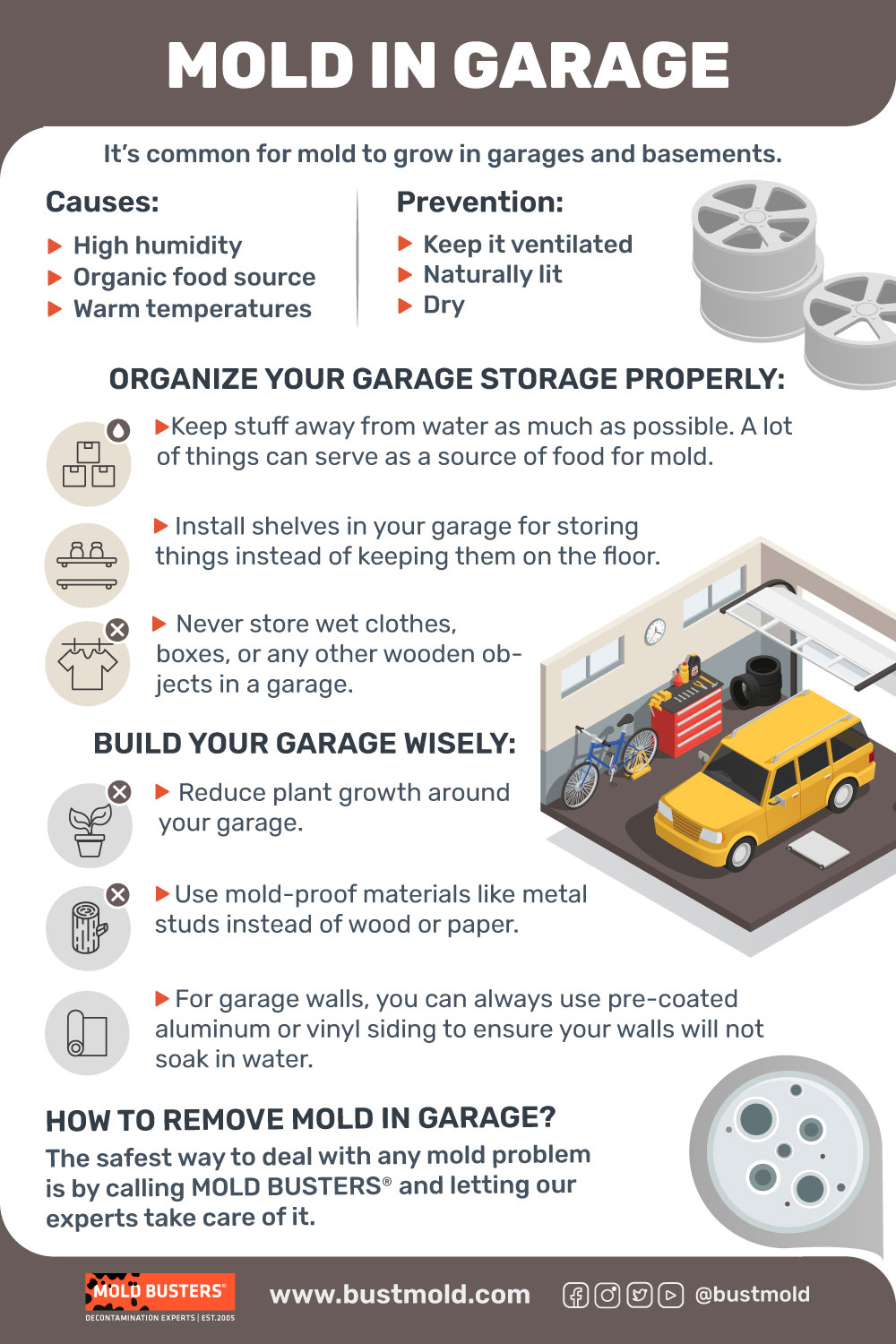
What Causes Mold Growth in Garages?
The Mold Triangle: Mold requires three elements to thrive—moisture, organic material (food source), and appropriate temperatures. Garages typically provide all three.
Moisture Sources in Garages
Water intrusion through poorly sealed garage doors represents the most common moisture source. During rain or snow, water seeps through degraded weather stripping around garage door perimeters. Vehicles parked after driving in wet conditions bring moisture inside—snow melting off cars in winter and rain runoff in other seasons create puddles that evaporate, raising humidity levels.
Roof leaks from damaged shingles, flashing failures, or gutter overflow send water down interior walls or create ceiling stains. Foundation cracks allow groundwater to penetrate, especially during heavy rainfall or spring thaw. Plumbing leaks from water heaters, utility sinks, or pipes running through garage spaces provide constant moisture to support mold growth.
Condensation forms when warm, humid air meets cold surfaces—particularly problematic in heated garages during winter months. Garage door panels, windows, and concrete floors become condensation collection points. Poor ventilation traps this moisture, preventing natural drying.
💧 Common Water Entry Points
- Poorly sealed garage doors
- Roof leaks from damaged shingles
- Foundation cracks
- Plumbing leaks
- Condensation on cold surfaces
🌡️ Temperature Issues
- Heated garages in winter
- Warm air meets cold surfaces
- Ice dams on roofs
- Thermal bridging
- Poor insulation
Ventilation and Air Circulation Problems
Most garages lack adequate ventilation, especially detached or older structures built without windows or vents. Stagnant air allows humidity to accumulate rather than dissipate. When humidity levels exceed 60%, mold spores activate and begin colonizing surfaces. Opening garage doors periodically helps, but many homeowners keep garages closed during extreme weather—precisely when moisture problems intensify.
Temperature Fluctuations and Seasonal Factors
Temperature differences between garage interiors and exterior conditions create ideal mold environments. Heated garages in winter experience condensation when warm interior air hits cold door panels. Unheated garages see moisture from melting snow accumulate without adequate evaporation. Summer heat combined with humidity from stored items creates greenhouse-like conditions perfect for rapid mold growth.
Storage Practices That Promote Mold
⚠️ High-Risk Storage Items: Cardboard boxes, papers, fabrics, wooden materials, wet boots and jackets, snow removal equipment, lawn care tools, and garbage all provide abundant organic matter for mold to consume.
Items stored directly on concrete floors trap moisture underneath. Cardboard boxes, papers, fabrics, and wooden materials provide abundant organic matter for mold to consume. Storing wet boots, jackets, snow removal equipment, or lawn care tools without proper drying allows mold to establish on these items and spread to surrounding surfaces. Garbage left in garages feeds mold colonies with organic waste materials.
For comprehensive assessment of moisture sources and mold risk factors specific to your garage, contact Mold Busters for a professional inspection. Our certified technicians identify all contributing factors and provide targeted remediation recommendations.
Where Does Mold Grow Inside a Garage?
Mold colonizes specific garage locations based on moisture availability, surface type, and light exposure. Understanding common growth areas helps you conduct thorough inspections.
Mold on Garage Ceilings

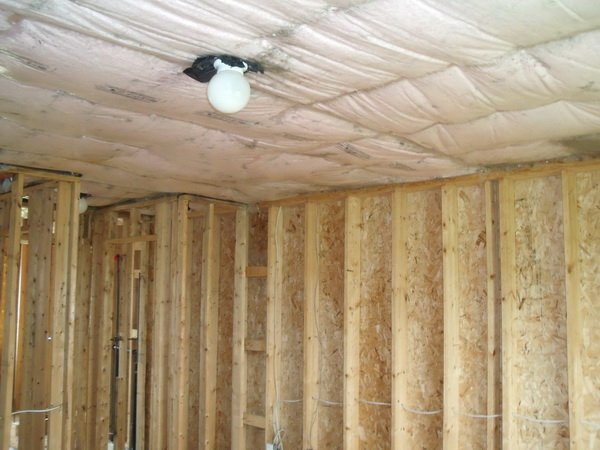
Garage ceilings, particularly in heated spaces, accumulate mold due to rising moisture from vehicle evaporation and poor attic insulation. When warm, humid air rises and meets cooler ceiling surfaces, condensation forms—creating perfect conditions for mold colonization. This problem intensifies in winter when temperature differentials are greatest.
Black mold on garage ceiling drywall typically indicates persistent moisture problems from roof leaks, inadequate ventilation, or thermal bridging through ceiling joists. Ceiling corners and areas above garage doors experience highest moisture exposure. If you notice mold spreading across ceiling panels or dark discoloration patterns, this signals serious moisture infiltration requiring immediate attention.
Professional Garage Ceiling Mold Removal
🚫 DIY Warning: DIY ceiling mold removal carries significant risks—disturbing ceiling mold releases spores downward into breathing zones, and working overhead limits visibility and control. Professional mold removal companies use containment barriers, negative air pressure systems, and HEPA filtration to prevent spore spread during ceiling remediation.
For black mold on garage ceilings, professional intervention is essential to ensure complete eradication and prevent recurrence. Contact our certified specialists for safe, effective ceiling mold remediation.
Mold on Garage Concrete Floors
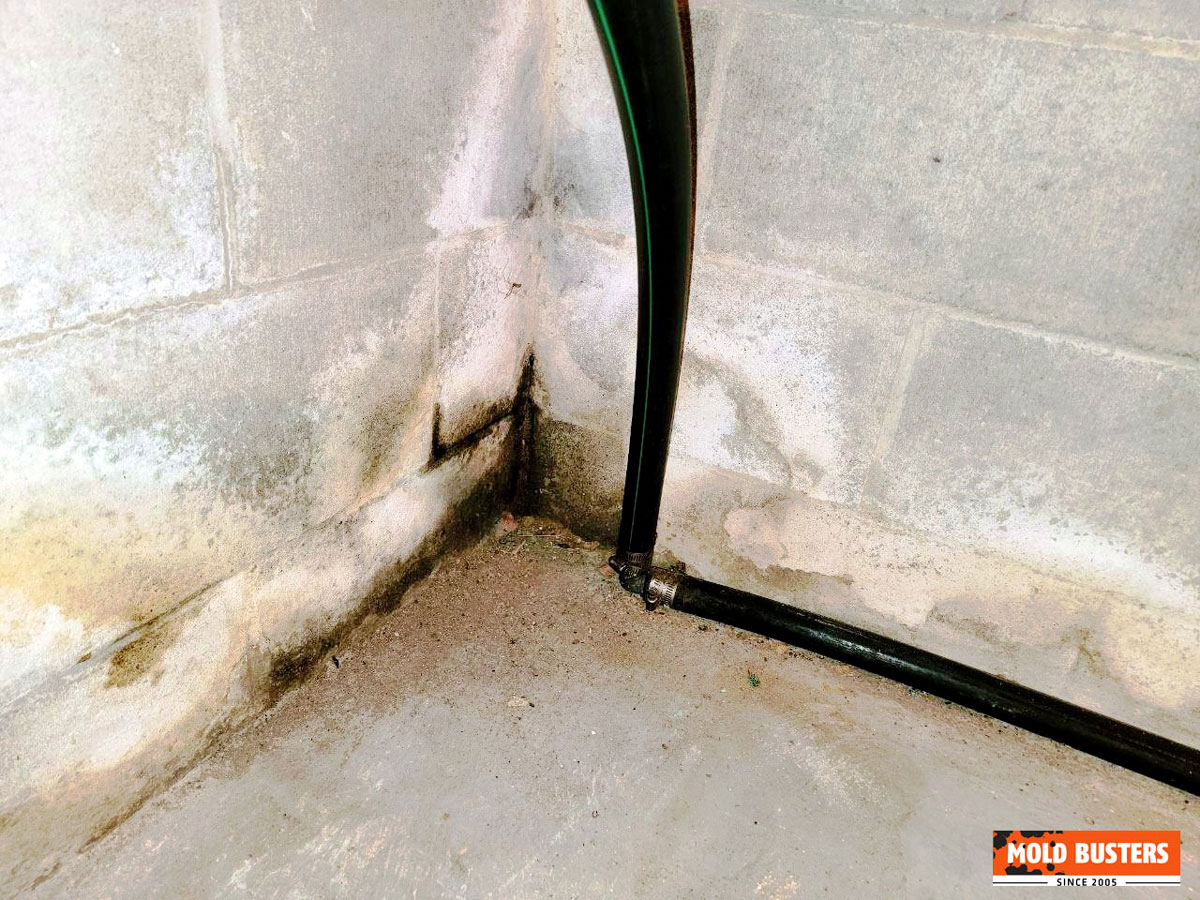

Despite appearing solid and impermeable, concrete absorbs moisture from groundwater, melting snow, and condensation. Concrete’s porous nature allows water to wick upward from the soil below, creating damp surface conditions ideal for mold. Dark discoloration on concrete floors near garage door entrances, corners, or along foundation perimeters often indicates mold colonization mixed with accumulated dirt and organic matter.
Removing Mold from Garage Floors
Small mold patches on concrete floors (under 10 square feet) may respond to DIY cleaning with distilled white vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, or commercial concrete cleaners. Scrub thoroughly with stiff brushes, rinse completely, and ensure the area dries fully. However, if mold returns quickly after cleaning, the moisture source remains unaddressed—requiring professional assessment to identify and correct underlying issues.
For extensive floor mold or situations where DIY attempts have failed, professional mold removal services provide comprehensive solutions including moisture barrier installation, crack sealing, proper drainage correction, and application of mold-resistant coatings.
Preventing Concrete Floor Mold
🛡️ Prevention Strategies
- Ensure proper garage floor slopes drain water toward exits
- Seal foundation cracks preventing groundwater intrusion
- Install vapor barriers beneath concrete during construction or renovation
- Use dehumidifiers maintaining humidity below 50%
- Avoid storing items directly on floors—use pallets or shelving
- Apply mold-resistant concrete sealers or epoxy coatings
Mold on Garage Walls and Drywall
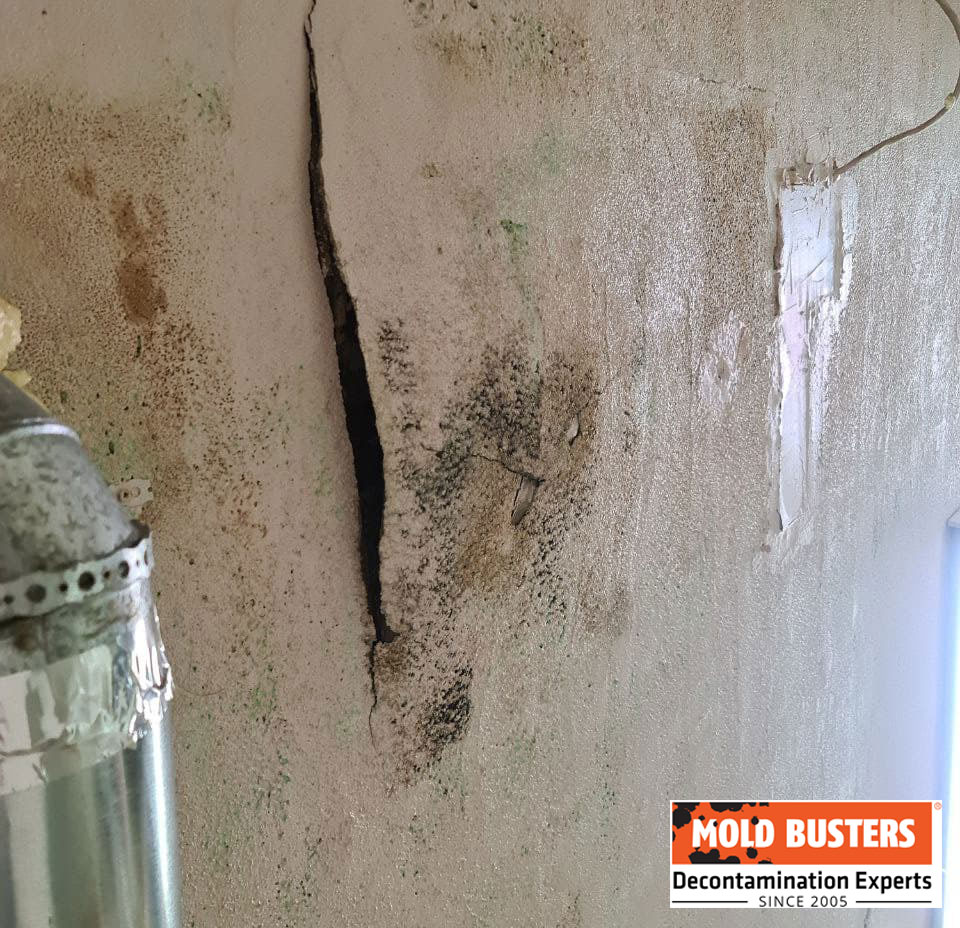

Drywall in garages presents significant mold vulnerability due to its paper facing providing perfect food sources for mold. Unfinished or poorly painted drywall absorbs moisture readily, accelerating colonization. Mold on garage drywall appears as discoloration, fuzzy patches, or dark staining spreading from corners, floor lines, or behind stored items leaning against walls.
If drywall was installed without proper priming and painting using quality, moisture-resistant products, porosity increases dramatically. Even painted drywall develops mold when water intrusion occurs from roof leaks, foundation issues, or persistent high humidity. Keeping wet or damp items away from walls and ensuring adequate air circulation between stored materials and wall surfaces helps prevent wall mold establishment.
Mold on Radon Mitigation Pipes
Radon pipes installed in garages create unique mold growth opportunities. These pipes extract cold air from beneath building foundations and exhaust it above roof lines. Temperature differentials between cold pipe surfaces and warm garage air cause condensation to form on pipe exteriors. When dust particles accumulate on condensation-coated pipes, mold finds both moisture and food sources.
Prevent radon pipe mold by wiping pipes weekly with dry cloths to remove dust accumulation, insulating exposed pipe sections to minimize condensation, and ensuring adequate garage ventilation to reduce overall humidity. If mold appears on radon pipes despite these measures, underlying humidity problems require professional assessment.
Mold on Garage Doors
Garage doors experience intense temperature fluctuations, especially in heated garages during winter. Minimal insulation in standard garage doors creates cold interior surfaces where warm, humid air condenses. This condensation provides moisture for mold colonization on door panels, weather stripping, and frame components.
Poor weather stripping allows rain and snow infiltration around door perimeters, wetting door frames and adjacent wall materials. Accumulated dust and organic debris on door surfaces supply food sources for mold once moisture appears. Professional garage door service companies can adjust door alignment, replace degraded weather stripping, and improve sealing to prevent moisture intrusion and subsequent mold growth.
Mold on Stored Items and Personal Belongings
Garages serve as storage spaces for seasonal items, sporting equipment, tools, and household overflow. Unfortunately, many stored items create or exacerbate mold problems. Wet boots, jackets, snow removal equipment, and lawn care tools brought into garages carry moisture that evaporates, raising ambient humidity. Items stored in cardboard boxes absorb moisture and provide substantial organic material for mold feeding.
Clothing and fabric items left damp develop mold quickly, spreading to surrounding materials. Wooden furniture, cases, and construction materials stored in garages experience mold colonization when humidity remains elevated. Using boot dryers for wet footwear, storing items in sealed plastic containers rather than cardboard, elevating storage on shelves rather than floors, and ensuring items are completely dry before garage storage significantly reduces mold risk on personal belongings.
Common Types of Mold Found in Garages
Various mold species colonize garage environments depending on available materials, moisture levels, and temperature conditions. Identifying mold type helps determine appropriate remediation approaches and health risk assessments.
| Mold Type | Characteristics | Health Risks | Recommended Removal Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Mold (Stachybotrys) |
Dark black or greenish-black Slimy texture |
Respiratory disorders Asthma attacks Allergic reactions |
Professional mold removal Use of hydrogen peroxide or distilled white vinegar |
| Green Mold (Cladosporium) |
Olive-green to brown or black Powdery or suede-like texture |
Skin rashes Sore throat Eye irritation |
Scrubbing with mold removal product Proper ventilation |
| White Mold | White and powdery Can grow on any organic material |
Allergic reactions Respiratory issues |
Scrubbing with mild detergent Ensure area is dry and free from moisture |
| Yellow Mold (Aspergillus) |
Bright yellow or green Can appear in spots |
Lung infections Allergic reactions |
Professional mold removal Use of mold-resistant materials |
Black Mold in Garages
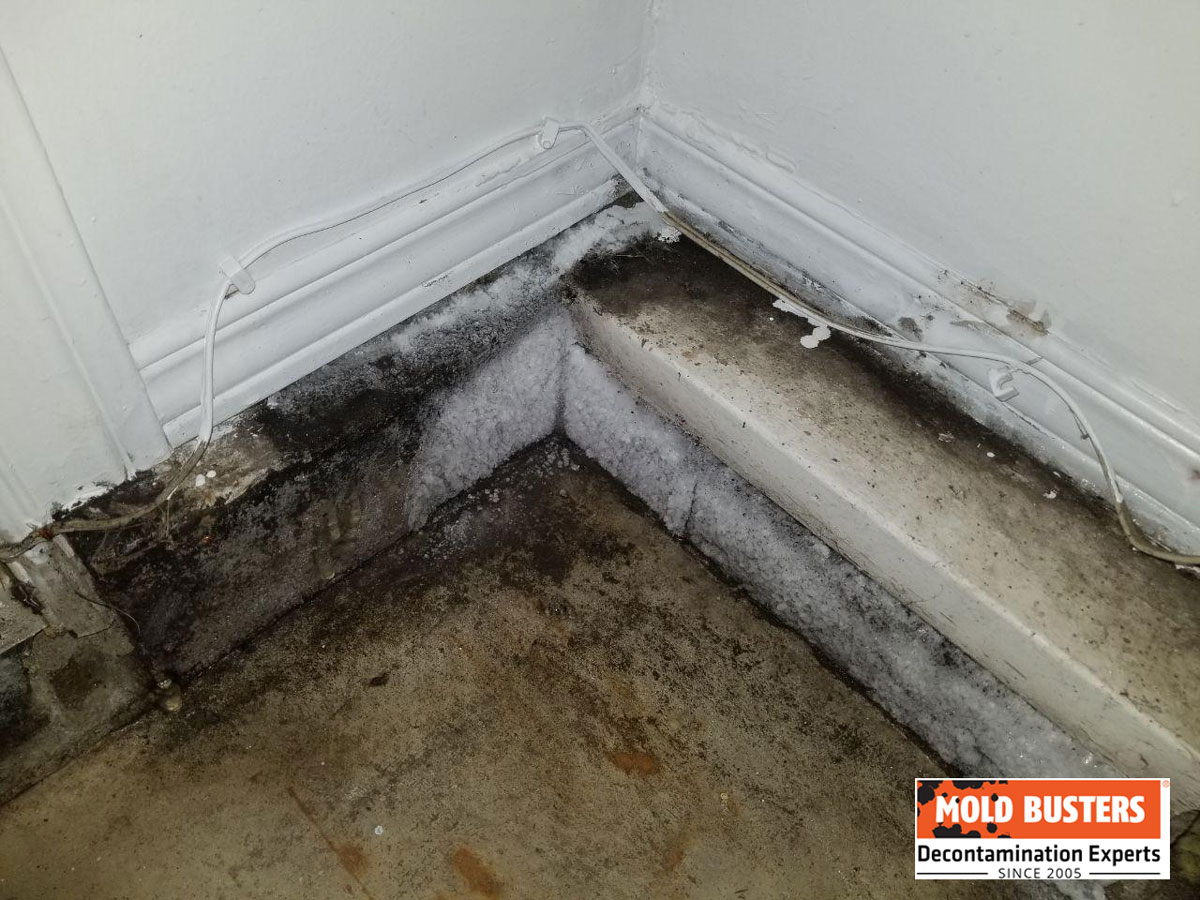

Black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) grows on materials with high cellulose content like drywall paper, wood, and cardboard in persistently damp conditions. This species produces mycotoxins potentially causing serious health effects. Black mold appears dark greenish-black with slimy texture, grows in circular patterns, and emits a particularly strong musty odor.
⚠️ Safety Warning: Never touch suspected black mold without proper personal protective equipment (respirator, gloves, eye protection) as disturbing colonies releases massive spore quantities.
Green Mold Species
Green mold encompasses over 100 species, most commonly Cladosporium, Aspergillus, and Penicillium. These molds range from olive-green to blue-green coloring and may resemble algae growth. Green molds typically cause allergic reactions and respiratory irritation rather than toxic effects, though immunocompromised individuals face elevated risks. Cladosporium grows on both porous and non-porous surfaces, making it one of the most prevalent garage molds.
White Mold Identification
White mold appears powdery or cotton-like, often mistaken for efflorescence (mineral salt deposits) on concrete. Key distinction: efflorescence is crystalline and crushes to powder easily, while mold maintains fibrous texture and typically has musty odor. White mold grows on various surfaces including wood, drywall, concrete, and fabrics. Though generally less harmful than black mold, white mold still triggers allergic responses and requires removal.
If you’ve discovered odd-looking growth in your garage and are uncertain about identification, Mold Busters professionals conduct thorough inspections with laboratory testing to definitively identify mold species. Proper identification guides remediation strategy and health risk assessment.
How to Remove Mold from Your Garage: DIY vs Professional
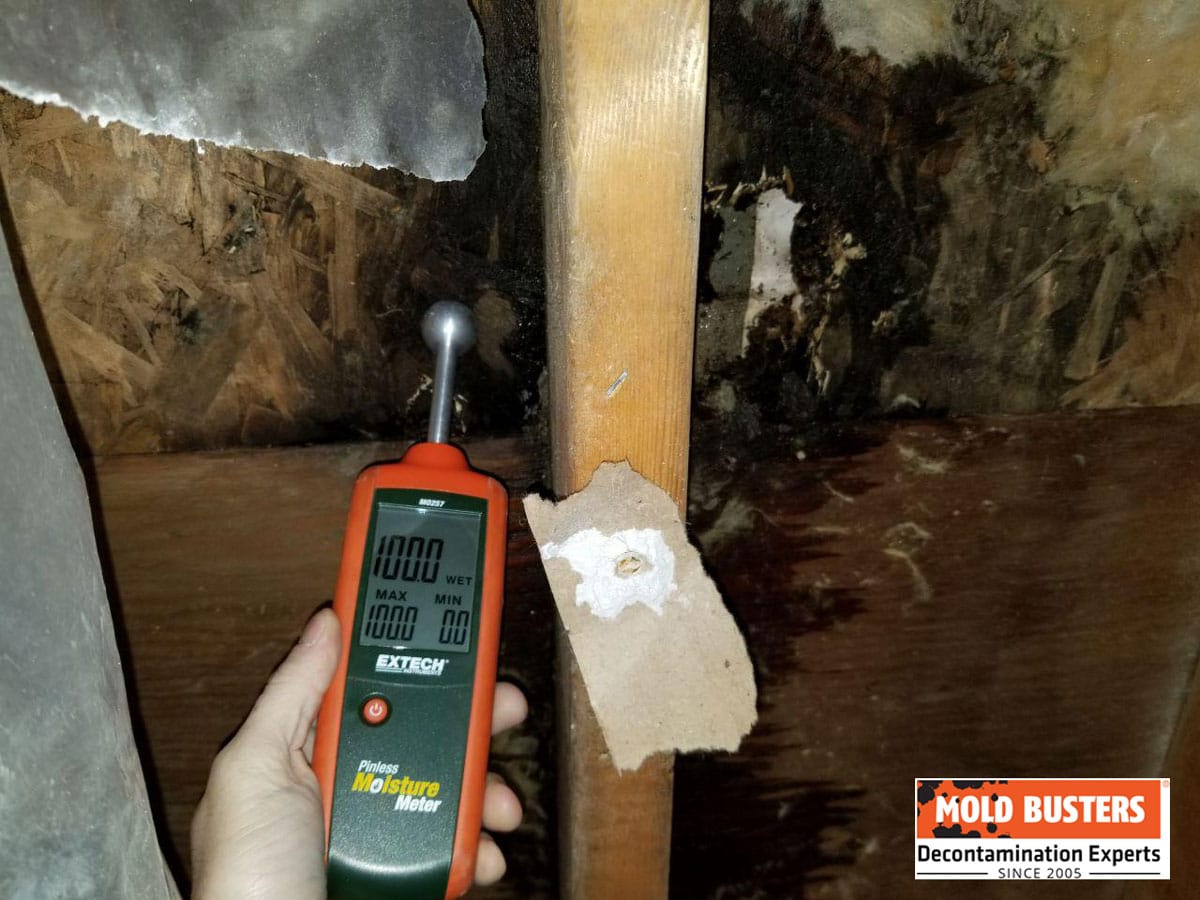

Deciding between DIY mold removal and professional remediation depends on several critical factors including mold extent, surface types affected, health risks present, and moisture source complexity.
When DIY Mold Removal Is Appropriate
✅ DIY is suitable when: Mold growth is limited (under 10 square feet total), affects only non-porous or semi-porous surfaces like concrete or painted wood, resulted from a one-time moisture event now corrected, and involves low-toxicity mold types (not black mold). Additionally, no household members have respiratory conditions, immune system compromises, or severe mold allergies, and you possess proper safety equipment including N95 or N100 respirator, rubber gloves, eye protection, and protective clothing.
DIY Garage Mold Removal Process
If attempting DIY removal, follow this systematic approach. First, ensure safety by wearing proper protective equipment (respirator, gloves, eye protection), ventilating the space by opening garage doors and windows, and isolating the work area with plastic sheeting to prevent spore spread.
🛡️ Safety Equipment
- N95 or N100 respirator
- Rubber gloves
- Eye protection
- Protective clothing
- Ventilate the space
🧴 Cleaning Solutions
- Distilled white vinegar (undiluted)
- Hydrogen peroxide (3-10%)
- Commercial mold removers
- 15-60 minutes contact time
- Scrub thoroughly
🗑️ Disposal Process
- Seal contaminated materials in bags
- Dispose in outdoor trash
- Never use standard vacuums
- HEPA-filtered only
- Identify moisture sources
For cleaning, prepare solutions such as distilled white vinegar (undiluted in spray bottles), hydrogen peroxide (3-10% solutions), or commercial mold removers following manufacturer instructions. Apply cleaning solution generously to affected areas, allow 15-60 minutes contact time for penetration, scrub thoroughly using stiff brushes (disposable if possible), and remove loosened mold with disposable cloths.
Finally, prevent recurrence by identifying and correcting moisture sources (leaks, condensation, poor drainage), improving ventilation through windows, vents, or dehumidifiers, and applying mold-resistant coatings to surfaces after complete drying.
When Professional Mold Removal Is Necessary
🚨 Professional help required when: Mold covers more than 10 square feet, black mold or toxic species are present, mold has penetrated porous materials like drywall or insulation, the moisture source is complex (foundation issues, persistent leaks, drainage problems), household members have health vulnerabilities, mold returns repeatedly after DIY cleaning attempts, or you lack proper safety equipment or remediation knowledge.
🏆 Professional Remediation Services Include:
- ✓ Thorough mold inspection with moisture mapping
- ✓ Laboratory testing for species identification
- ✓ Containment using negative air pressure systems
- ✓ Complete mold removal with HEPA filtration
- ✓ Treatment of affected materials with antimicrobial applications
- ✓ Moisture source correction recommendations
- ✓ Post-remediation verification testing
- ✓ Extended warranties on remediation work
For professional assessment and remediation services across Ontario and Quebec, Mold Busters provides certified, experienced technicians using industry-leading techniques and equipment. We offer free virtual inspections to assess your situation and provide detailed remediation proposals.
Comparing DIY and Professional Mold Removal
| Criteria | DIY Mold Removal | Professional Mold Removal |
|---|---|---|
| Tools & Materials | Distilled white vinegar Hydrogen peroxide Mild detergent Scrubbing brushes |
Specialized mold removal products Industrial-grade equipment Protective gear |
| Effectiveness | Effective for small mold patches Might not eliminate mold spores completely |
Comprehensive removal Ensures complete eradication of mold and spores |
| Cost | $50-$200 Cleaning supplies and protective equipment |
$500-$6,000+ Based on extent and complexity |
| Safety | Potential exposure to mold spores Risk of using harmful chemicals without proper protection |
Professionals use protective gear Safe removal without risk to homeowners |
| Time Consumption | 4-8 hours for small areas Multiple treatments might be required |
1-3 days typically Usually requires one intervention |
| Post-Removal Support | DIY tips for preventing future mold growth Limited to general knowledge |
Expert advice on preventing mold recurrence Warranties and follow-up verification |
How Much Does Professional Garage Mold Removal Cost?
Typical Cost Ranges: Small projects (under 10 sq ft): $500-$1,500 | Medium projects (10-100 sq ft): $1,500-$3,500 | Large projects (100+ sq ft): $3,500-$10,000+
Garage mold removal costs vary significantly based on multiple factors. Understanding typical price ranges helps you budget appropriately and evaluate remediation proposals.
Garage Mold Inspection Costs
Professional mold inspection services in Ontario and Quebec typically range from $300-$670. Basic visual inspections without sampling start around $300-$450. Comprehensive inspections including air or surface sampling with laboratory analysis range from $450-$670. Factors affecting inspection costs include garage size (larger spaces require more time), sampling requirements (each laboratory sample adds $50-$120), accessibility challenges, and travel distance from service centers.
Professional Mold Remediation Pricing
Under 10 square feet affected
- Limited mold growth
- Single area treatment
- Basic containment
- Surface cleaning
10-100 square feet
- Multiple areas affected
- Enhanced containment
- HEPA filtration
- Material removal
Over 100 square feet or whole-garage
- Extensive contamination
- Full containment systems
- Structural repairs
- Extended project timeline
Remediation costs depend on several variables. Small-scale remediation (under 10 square feet affected) typically costs $500-$1,500. Medium projects (10-100 square feet) range from $1,500-$3,500. Large-scale remediation (over 100 square feet or whole-garage projects) can cost $3,500-$10,000 or more.
Please Note: The costs mentioned in this article are average estimates. Actual costs can vary significantly based on the specifics of your mold remediation project. For an accurate quote, please contact us for a detailed assessment.
Cost Factors and Variables
📊 Factors Increasing Costs
- Mold type: Toxic species require enhanced protocols
- Affected materials: Porous materials like drywall cost more to remediate than concrete
- Moisture source correction: Foundation or drainage repairs add costs
- Containment requirements: Preventing spread in attached garages
- Disposal needs: Contaminated materials require special handling
Cost-Benefit Analysis: DIY vs Professional
💰 Investment in Professional Services
While DIY approaches cost $50-$200 in supplies and equipment, unsuccessful attempts lead to continued mold growth, potential health complications, and eventual professional services anyway—making total costs higher than immediate professional intervention.
Professional services provide: Guaranteed results with warranties, complete spore removal preventing recurrence, moisture source identification and correction guidance, and health protection for household members.
For detailed cost estimates specific to your garage mold situation, contact Mold Busters for a free consultation and comprehensive assessment. We provide transparent pricing with detailed remediation proposals explaining all recommended work.
How to Prevent Mold Growth in Your Garage

Prevention is better than remediation: Implementing comprehensive moisture control and environmental management strategies keeps garages mold-free long-term, protecting your health and preserving property value.
Prevention delivers far better outcomes than remediation. Implementing comprehensive moisture control and environmental management strategies keeps garages mold-free long-term. Mold prevention protects your health, preserves stored items, and maintains property value.
1. Conduct Regular Garage Inspections
Systematic monthly inspections identify moisture problems before mold establishes. Check garage roofs for missing shingles, damaged flashing, or sagging areas indicating water damage. Inspect gutters for clogs, damage, or improper drainage directing water toward garage foundations. Examine walls and ceilings for water stains, discoloration, or soft spots suggesting hidden leaks. Test garage door weather stripping by closing doors and looking for light gaps indicating seal failures.
🔍 Key Inspection Areas: Pay particular attention to roof-wall junctions, corners where moisture accumulates, areas around utility penetrations (pipes, vents, electrical), and foundation perimeters where groundwater intrusion occurs. Small leaks detected early cost far less to repair than extensive mold remediation later.

Garage Mold
2. Install Effective Drainage Systems
Water entering garages accelerates mold growth dramatically. Multiple water entry points require attention including precipitation (rain and snow), vehicle moisture (melting snow, rain runoff), and groundwater intrusion through foundations.
💧 Drainage Solutions
- Proper floor slope (1% grade minimum)
- Floor drains in low points
- Extend downspouts 6-10 feet away
- Seal foundation cracks
- Consider French drains
🌊 Water Entry Prevention
- Keep drains clear of debris
- Direct water away from structures
- Use hydraulic cement for active leaks
- Epoxy/polyurethane for stable cracks
- Maintain proper grading
Ensure garage floors slope properly toward drainage points or exterior doors—minimum 1% grade (1/8 inch per foot) facilitates water flow rather than pooling. Install or maintain floor drains in garage centers or low points, keeping drains clear of debris. Extend downspouts at least 6-10 feet from garage foundations, directing water away from structures. Seal foundation cracks with appropriate materials (hydraulic cement for active leaks, epoxy or polyurethane for stable cracks).
3. Organize Storage to Minimize Mold Risk
Storage practices significantly impact garage mold development. Many items serve as food sources for mold once moisture appears.
✅ Best Practices
- Elevate all storage using metal or plastic shelving units
- Use sealed plastic containers instead of cardboard
- Maintain 3-4 inch air gaps from walls
- Keep humidity below 50% with dehumidifiers
- Keep belongings dry
❌ Items to Avoid Storing
- Paper products and cardboard boxes
- Fabrics and textiles
- Wood furniture
- Leather goods (unless climate-controlled)
- Wet or damp items of any kind
Elevate all storage using metal or plastic shelving units—never store items directly on concrete floors where moisture accumulates. Use sealed plastic containers instead of cardboard boxes for long-term storage. Cardboard absorbs moisture and provides substantial organic material for mold feeding. Maintain air gaps between stored items and walls (minimum 3-4 inches) allowing air circulation and preventing moisture trapping.
4. Control Humidity and Improve Ventilation

Black mold in garage
Moist, dark, confined, and stuffy environments create perfect mold development conditions. Garages naturally tend toward these characteristics unless actively managed.
High humidity represents one of the most common mold causes. Many garages lack windows, air vents, or adequate air circulation.
💨 Humidity Control
- Install dehumidifiers (30-50% humidity)
- Empty collection buckets regularly
- Use continuous drain options
- Monitor humidity levels consistently
🌬️ Ventilation Strategies
- Open doors/windows 2-3 hours daily
- Install passive vents in walls/gables
- Exhaust fans with humidity sensors
- Ventilate after parking wet vehicles
To reduce humidity effectively, install dehumidifiers maintaining levels between 30-50%. Portable dehumidifiers work well for most residential garages—empty collection buckets regularly or use continuous drain options.
Improve natural ventilation by opening garage doors or windows for 2-3 hours daily when weather permits, especially after parking wet vehicles. Install passive vents in garage walls or gables allowing continuous air exchange without compromising security. Consider exhaust fans with humidity sensors automatically activating when moisture levels rise.
5. Build or Renovate with Mold-Resistant Materials
New garage construction or renovation projects present opportunities to prevent mold from the outset using appropriate materials and construction techniques.
🏗️ Mold-Resistant Materials
- Use mold-resistant drywall (purple board or paperless drywall)
- Choose metal studs rather than wood framing where possible
- Apply mold-resistant paint or coatings containing antimicrobial additives
- Use concrete sealers or epoxy floor coatings
- Install pre-coated aluminum or vinyl siding
Use mold-resistant drywall (purple board or paperless drywall) instead of standard paper-faced drywall. These products use fiberglass mat facings or specialized treatments resisting mold growth even when damp. Choose metal studs rather than wood framing where possible—metal cannot support mold growth while wood provides substantial organic material.
Though mold-resistant materials cost modestly more initially, they deliver substantial long-term value through mold prevention, eliminating expensive remediation needs later.
6. Manage Landscaping Around Your Garage
Vegetation near garage structures contributes to moisture problems and mold growth through multiple mechanisms.
🌿 Landscaping Best Practices: Trim shrubs and plants maintaining minimum 18-24 inch clearance from garage walls. Dense vegetation traps moisture against structures, reduces air circulation, and prevents sunlight from drying damp surfaces. Overhanging tree branches drop leaves into gutters causing clogs and water overflow onto garage roofs. Remove climbing vines from garage exteriors—while aesthetically pleasing, vines trap moisture and their roots penetrate wall materials causing structural damage and water entry points.
Additional Mold Prevention Strategies
Beyond primary prevention methods, these supplementary strategies further reduce mold risk:
- Place moisture absorbers (silica gel, activated alumina, anhydrous calcium sulfate, or molecular sieves) in strategic garage locations, particularly corners and enclosed spaces. Replace or regenerate desiccants regularly as they become saturated.
- Extend gutter downspouts 6-10 feet from garage foundations preventing moisture buildup around building bases. Use splash blocks or underground drain extensions directing water well away from structures.
- Never store wet clothing, jackets, shoes, wooden cases, boxes, or similar items in garages without proper drying. All materials entering garage storage must be completely dry. Use boot dryers or designated drying areas for wet items before storage.
- Address vehicle moisture promptly by allowing wet vehicles to dry outside before parking in garages when practical, using absorbent mats beneath vehicles catching dripping water, and running dehumidifiers after parking wet vehicles in enclosed garages.
- Insulate heated garages properly to minimize condensation from temperature differentials, particularly on garage door panels and ceiling surfaces.
Attached vs Detached Garages: Different Mold Considerations
Garage attachment to your home creates distinct mold risks and prevention requirements compared to detached structures. Understanding these differences helps you implement appropriate strategies.
Mold Risks in Attached Garages
⚠️ Higher Risk Alert: Attached garages pose elevated concerns because mold spores and odors easily migrate into living spaces through shared walls, doorways, and ventilation systems. Even with closed doors, air pressure differences, HVAC system connections, and wall penetrations allow contaminants to spread. Family members experience increased exposure when garage mold goes unaddressed.
Attached garages typically benefit from better temperature control (they’re often partially heated) but this creates condensation issues. Warm air from homes meeting cold garage surfaces produces moisture. Shared foundation walls between garages and basements allow moisture transmission in both directions—basement mold problems often correlate with garage moisture issues.
Mold Prevention for Attached Garages
🔒 Seal and Protect
- Seal all penetrations between garages and living spaces
- Install high-quality weather stripping on connecting doors
- Replace weather stripping annually
- Check regularly for cracks or gaps in shared walls
💨 Ventilation Solutions
- Install exhaust fans vented directly outdoors
- Run dehumidifiers continuously during humid seasons
- Maintain humidity below 50%
- Use mold-resistant paint on drywall
Seal all penetrations between garages and living spaces using appropriate materials (spray foam for utility penetrations, weather stripping for doors). Install high-quality weather stripping on doors between garages and homes, replacing annually. Consider installing exhaust fans vented directly outdoors rather than into attics or living spaces.
Detached Garage Mold Challenges
Detached garages face different issues. They typically lack heating, creating wide temperature fluctuations that promote condensation. Without regular occupant presence, moisture problems go unnoticed longer, allowing extensive mold establishment before discovery. Limited electrical service may restrict dehumidifier or ventilation fan installation.
However, detached garages pose less direct health risk to home occupants—mold spores remain contained unless transferred on clothing, tools, or stored items. This creates a decision point: some property owners accept cosmetic garage mold if it remains contained and doesn’t affect stored valuables, while others maintain detached garages to the same standards as attached structures.
Finished vs Unfinished Garage Spaces
🏠 Finished Garages
- More complex mold scenarios
- Finished surfaces hide moisture problems
- Insulation traps moisture
- Requires active moisture management systems
🔧 Unfinished Garages
- Allow visible moisture detection
- Easier remediation when problems arise
- Typically worse humidity control
- More favorable conditions for mold despite easier detection
If finishing garage spaces, use exclusively mold-resistant materials: paperless drywall, mold-resistant insulation (closed-cell spray foam rather than fiberglass), mold-inhibiting paint, and moisture barriers. Budget for mechanical ventilation and dehumidification—finished garages require active moisture management systems.
When to Call Professional Mold Remediation Services
Recognizing situations requiring professional intervention protects your health, prevents property damage escalation, and ensures complete mold elimination.
🚨 Call Professionals Immediately If:
- Mold covering more than 10 square feet (equivalent to a 3×3 foot area)
- Suspect or confirm black mold (Stachybotrys) presence based on color, texture, or smell
- Mold has penetrated building materials (growing inside walls, ceiling cavities, or insulation)
- Cannot identify or correct the moisture source causing mold growth
- Anyone in your household has respiratory conditions (asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis)
- Anyone has immune system compromises or severe mold allergies
- Mold returns repeatedly after DIY cleaning attempts
- You lack proper safety equipment (respirators, containment supplies, HEPA filtration)
- Selling or buying property requiring mold clearance documentation
🏆 Why Choose Mold Busters?
- ✓ Over 15,000 mold inspections across Ontario and Quebec
- ✓ Certified technicians with industry-leading expertise
- ✓ Thorough inspection identifying all mold-affected areas and moisture sources
- ✓ Containment preventing spore spread during remediation
- ✓ Industrial equipment (HEPA filters, negative air machines, commercial dehumidifiers)
- ✓ Antimicrobial treatments eliminating mold at root level
- ✓ Post-remediation verification testing confirming complete removal
- ✓ Extended warranties on all remediation work
- ✓ Serving Montreal, Ottawa, and surrounding areas
Mold Busters provides fast, effective, and affordable mold removal and remediation services for garages throughout Ontario and Quebec. Our certified technicians use industry-leading techniques and equipment ensuring complete mold elimination. If you’re in the Montreal or Ottawa area and suspect garage mold growth, contact us for professional assessment and remediation services.
Frequently Asked Questions About Garage Mold
For small mold patches on garage doors (under 10 square feet), homeowners can carefully attempt removal using proper safety equipment. Wear N95 respirator, rubber gloves, and eye protection before starting. Spray affected areas with undiluted white vinegar until thoroughly saturated. Vinegar’s acetic acid kills mold spores effectively. Allow one hour contact time, then carefully wipe away mold using disposable cloths. Immediately seal used cloths in plastic bags and dispose in outdoor trash. Wipe surfaces again with clean water, then dispose of cleaning cloths similarly. Vinegar odor dissipates within 2-3 hours. For extensive mold growth, suspected black mold, or if DIY attempts fail, contact Mold Busters for professional inspection and removal. We also offer virtual inspection services for convenient preliminary assessments.
Musty mold odors result from microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) that mold releases during growth. Eliminating the smell requires removing the source—you cannot mask or cover mold odors successfully without addressing underlying growth. First, locate and remove all visible mold following proper remediation procedures or hiring professionals for extensive problems. After mold removal, address residual odors through improved ventilation (open doors and windows for extended periods), running dehumidifiers to reduce humidity below 50%, using air scrubbers with HEPA and carbon filters capturing remaining spores and odor molecules, and cleaning all garage surfaces including walls, floors, and ceilings with appropriate solutions. If odors persist after thorough cleaning and dehumidification, hidden mold likely remains behind walls, in insulation, or other concealed areas. Professional inspection with moisture meters and thermal imaging identifies hidden mold sources. Mold Busters professionals ensure complete mold removal and source correction, permanently eliminating musty odors.
Yes, garage mold readily spreads to attached homes through several transmission methods. Mold spores are extremely small (2-100 microns) and lightweight, easily becoming airborne. Air currents created by opening doors, walking through spaces, or HVAC system operation transport spores from garages into living areas. Spores also transfer on clothing, footwear, tools, and items moved between garages and homes. Even small disturbances near mold colonies—brushing against affected surfaces or handling contaminated materials—release thousands of spores that attach to clothing and travel indoors. Shared walls between attached garages and homes allow spore migration through cracks, gaps around penetrations (electrical, plumbing, HVAC), and porous building materials. If garage mold remains unaddressed, gradual contamination of adjacent living spaces becomes inevitable. Prevent spread by addressing garage mold immediately upon discovery, sealing all penetrations between garages and homes, installing and maintaining weather stripping on connecting doors, removing shoes and outerwear before entering homes from garages, and running air purifiers with HEPA filters in rooms adjacent to garages. If you’ve discovered mold in an attached garage, contact Mold Busters promptly for professional remediation preventing spread into your living spaces.
Using mold-resistant drywall (purple board or paperless drywall) in garage construction or renovation significantly reduces mold growth risk. Standard drywall uses paper facing providing substantial organic food source for mold when moisture appears. Mold-resistant alternatives use fiberglass mat facing or specialized treatments resisting mold colonization even during damp conditions. Mold-resistant drywall proves particularly valuable in high-moisture areas including garages (frequent wet vehicle parking, humidity fluctuations, potential water intrusion), bathrooms (shower steam, high humidity), basements (foundation moisture, potential flooding), and kitchens (cooking moisture, plumbing proximity). However, mold-resistant drywall doesn’t eliminate mold risk entirely—it only slows mold establishment. Proper ventilation, humidity control (maintaining 30-50% relative humidity), and temperature management remain essential even with mold-resistant materials. If you’re constructing or remodeling, combine mold-resistant drywall with other prevention strategies including mechanical ventilation, dehumidification systems, mold-resistant paint, proper moisture barriers, and adequate drainage.
Professional garage mold removal costs vary based on multiple factors making generalized pricing difficult. Project scope determines cost more than any other factor. Typical price ranges include inspection and assessment ($300-$670) covering visual inspection, moisture mapping, and optional laboratory sampling. Small remediation projects (under 10 square feet affected) cost $500-$1,500. Medium projects (10-100 square feet) range from $1,500-$3,500. Large-scale remediation (over 100 square feet or full garage) costs $3,500-$10,000+. Cost factors include mold type (toxic species requiring enhanced protocols increase costs), affected materials (porous materials like drywall cost more than concrete remediation), moisture source (complex drainage or foundation issues add correction costs), containment requirements (preventing spread to living areas in attached garages), disposal needs (contaminated materials require special handling), and access challenges (limited access or high ceilings increase labor time). For accurate project-specific estimates, contact Mold Busters for free consultation and comprehensive assessment. Our thorough inspections identify all affected areas and moisture sources, enabling precise remediation proposals with transparent pricing explaining all recommended work. We serve property owners throughout Ontario and Quebec with professional, certified mold remediation services.
Black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) produces mycotoxins potentially causing serious health effects particularly with prolonged exposure. While not all black-colored mold is toxic Stachybotrys—other species produce dark coloring—actual Stachybotrys presents legitimate health concerns including respiratory disorders (chronic coughing, difficulty breathing, lung inflammation), allergic reactions (skin rashes, eye irritation, severe allergies), neurological symptoms (headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, memory problems), fatigue and weakness (chronic exhaustion, immune system suppression), and in extreme cases, pulmonary hemorrhage (bleeding in lungs, typically in infants or immunocompromised individuals). Health risks increase with exposure duration, mold concentration, individual sensitivity (children, elderly, immunocompromised face higher risks), and proximity to mold source (garages used frequently present greater exposure than occasional access). If you suspect black mold based on appearance (dark greenish-black coloring, slimy texture, strong musty odor), never attempt DIY removal. Disturbing black mold releases massive spore quantities dramatically increasing exposure. Instead, isolate the affected area (close doors, avoid disturbing mold), minimize garage use until remediation occurs, and contact professional mold remediation services immediately. Professionals use containment, negative air pressure, HEPA filtration, and antimicrobial treatments ensuring safe black mold removal without exposing occupants to health hazards.
Winter garage ceiling mold results primarily from condensation when warm, humid indoor air meets cold ceiling surfaces. This occurs most commonly in heated attached garages where temperature differentials are greatest. As wet vehicles enter heated garages, snow and ice melt, creating moisture that evaporates raising indoor humidity. This warm, moist air rises (heat rises naturally) and contacts cold ceiling materials. When air temperature drops below the dew point at ceiling surfaces, water condenses—providing moisture for mold colonization. Additional winter mold causes include inadequate attic insulation above garage ceilings (allows heat loss creating cold ceiling surfaces), roof leaks from ice dams (melting snow refreezes at eaves, forcing water under shingles), poor ventilation (trapped moisture cannot escape), thermal bridging through ceiling joists (creates cold spots where condensation concentrates), and heating systems without humidity control (raise indoor moisture without managing condensation risk). Prevent winter ceiling mold by improving attic insulation (maintain warm ceiling surfaces), installing vapor barriers (prevent moisture migration into ceiling cavities), improving ventilation (use exhaust fans removing humid air), addressing ice dams (improve roof ventilation and insulation), running dehumidifiers (maintain 30-40% relative humidity in winter), and allowing vehicles to drip dry outside before parking in heated garages when practical.

Get Special Gift: Industry-Standard Mold Removal Guidelines
Download the industry-standard guidelines that Mold Busters use in their own mold removal services, including news, tips and special offers:
"*" indicates required fields
Published: May 19, 2020 Updated: October 9, 2025

Written by:
Steven Adams
AMRT, WRT, ASD
Mold Busters
Fact checked by:
Michael Golubev
CEO
Mold Busters

