Black Mold: Identification, Health Risks & Professional Removal
Expert guide to recognizing toxic black mold, understanding its dangers, and protecting your family with professional remediation
If you’ve spotted dark, clustered growths in your home, you’re right to be concerned. Black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) is one of the most toxic mold species found in homes across Ontario and Quebec. Unlike regular household molds that cause minor allergies, black mold produces dangerous mycotoxins that can cause serious respiratory problems, chronic fatigue, and neurological issues—especially in children, elderly individuals, and those with compromised immune systems.
⚠️ Worried About Black Mold? Get a Free Inspection!
Black mold is highly toxic and can pose serious health risks. Contact Mold Busters for a free virtual mold inspection. Our certified experts will provide a comprehensive assessment and customized remediation plan.
What is Black Mold?
Black mold, scientifically known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a toxic fungus that produces harmful mycotoxins. Unlike common household molds, black mold releases toxins capable of causing serious respiratory problems, chronic fatigue, and neurological issues.
Black mold appears as dark greenish-black colonies with a slimy texture when actively growing. When its water source dries up, it becomes dry and powdery but remains equally dangerous. According to our analysis of over 15,000 mold inspections since 2005, Stachybotrys chartarum ranks as the third most common toxic mold found in Canadian homes.
What Causes Black Mold?

🌊 Primary Causes of Black Mold Growth
- Prolonged moisture exposure: Water damage from flooding, leaks, burst pipes, or chronic condensation
- Delayed water damage response: When water seeps into materials like drywall or wood and remains for 24-48 hours
- Poor ventilation: Trapped moisture accelerates mold development
- High humidity: Levels above 60% provide the moisture black mold needs to thrive
Is Black Mold Dangerous to Your Health?
Yes, black mold is significantly more dangerous than regular household molds. It produces trichothecene mycotoxins that cause serious health problems when inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through skin contact. The severity depends on exposure duration, concentration levels, and individual sensitivity.
What makes it particularly concerning is that mycotoxins remain potent even after visible mold is removed. Disturbing black mold without proper containment releases millions of toxic spores into the air, where they circulate through HVAC systems throughout your home.
🚨 Vulnerable Populations at Greatest Risk
- Infants and young children
- Elderly individuals
- Pregnant women
- Anyone with compromised immune systems
- People with asthma or chronic respiratory conditions
These groups should avoid contaminated spaces entirely until professional remediation is completed.
What Does Black Mold Look Like?
Black mold appears as dark greenish-black or pure black patches with a slimy, wet texture when actively growing. Colonies form in irregular patterns rather than perfect circles, creating dense clusters that spread across affected surfaces. In high-humidity environments, black mold appears gelatinous and shiny. When moisture diminishes, it takes on a powdery, sooty appearance—but remains equally toxic.
🔍 Visual Identification Signs
- Dark greenish-black coloration
- Slimy or wet appearance with raised texture
- Musty earthy odor
- Spreading patterns following water damage
- Growth on cellulose materials like drywall and wood
⚠️ Harmless Black-Colored Mold
Not all black-colored mold is toxic Stachybotrys chartarum. Harmless species like Cladosporium appear dark but lack mycotoxin capability. These typically have olive-black or brownish coloring with powdery, velvety texture rather than the slimy appearance of Stachybotrys.
Professional laboratory testing is the only reliable identification method.
Black Mold vs. Regular Mold: What’s the Difference?

Black mold differs fundamentally from regular household molds in toxicity, appearance, and health impact. While common molds like Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Cladosporium primarily cause allergic reactions, black mold produces mycotoxins that can lead to serious neurological problems, chronic respiratory disease, and immune system suppression.
Key Differences
🎨 Appearance & Texture
Black mold: Dark greenish-black with distinctively slimy, wet texture.
Regular molds: Varied colors (white, green, gray, blue, brown) with fuzzy, powdery, or velvety textures.
☠️ Toxicity Levels
Black mold: Produces dangerous mycotoxins that remain hazardous even after the mold dies.
Regular molds: Don’t produce significant toxins; primarily affect individuals during active exposure.
📈 Growth Patterns
Black mold: Grows slowly but forms concentrated, dense colonies specifically on cellulose-rich materials.
Regular molds: Spread more quickly across surfaces in scattered patches covering wider areas.
👃 Smell Intensity
Black mold: Intensely strong, musty, earthy odor often described as rotting wood.
Regular molds: Milder musty smells that may not be noticeable unless directly near growth.
🏥 Health Impact
Black mold: Chronic fatigue, persistent headaches, difficulty concentrating, respiratory problems that don’t improve after leaving contaminated spaces.
Regular molds: Sneezing, itchy eyes, mild respiratory irritation that resolves once exposure ends.
🛠️ Removal Requirements
Black mold: Always requires professional remediation regardless of size, with strict containment protocols.
Regular molds: Small areas (under 10 sq ft) can sometimes be cleaned by homeowners with proper safety equipment.
Important: When you discover dark mold growth, don’t attempt species identification yourself. Professional mold inspection with laboratory analysis provides definitive identification and ensures appropriate remediation protocols.
What Does Black Mold Smell Like?
Black mold produces a distinctively strong, pungent odor often described as intensely musty, earthy, or similar to rotting wood and damp paper. This smell results from microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) released during metabolic processes. The odor is significantly stronger than mild mustiness associated with regular household molds.
Many describe it as similar to wet socks, damp basements, or decomposing organic material. The smell is most noticeable in enclosed spaces like closets, bathrooms without ventilation, and sealed basements. Even when hidden behind walls, the smell often permeates through materials.
The intensity correlates with colony size. Small, early-stage growth may produce only faint mustiness, while established colonies create persistent, overwhelming smell. If you notice persistent musty smell that intensifies over time, especially after water damage, professional inspection is warranted regardless of visible growth. The smell indicates active mycotoxin production—you’re inhaling these compounds along with potentially airborne spores.

Did you know?
Stachybotrys (black mold) is the 3rd most common toxic mold type found in homes we tested! Find out more exciting mold stats and facts inside our mold statistics page.
Black Mold Pictures & Identification Guide
Visual identification helps recognize potential problems, but laboratory testing provides the only definitive species identification. These images show black mold in various stages and locations commonly found in Ontario and Quebec homes.








How Fast Does Black Mold Spread and Grow?
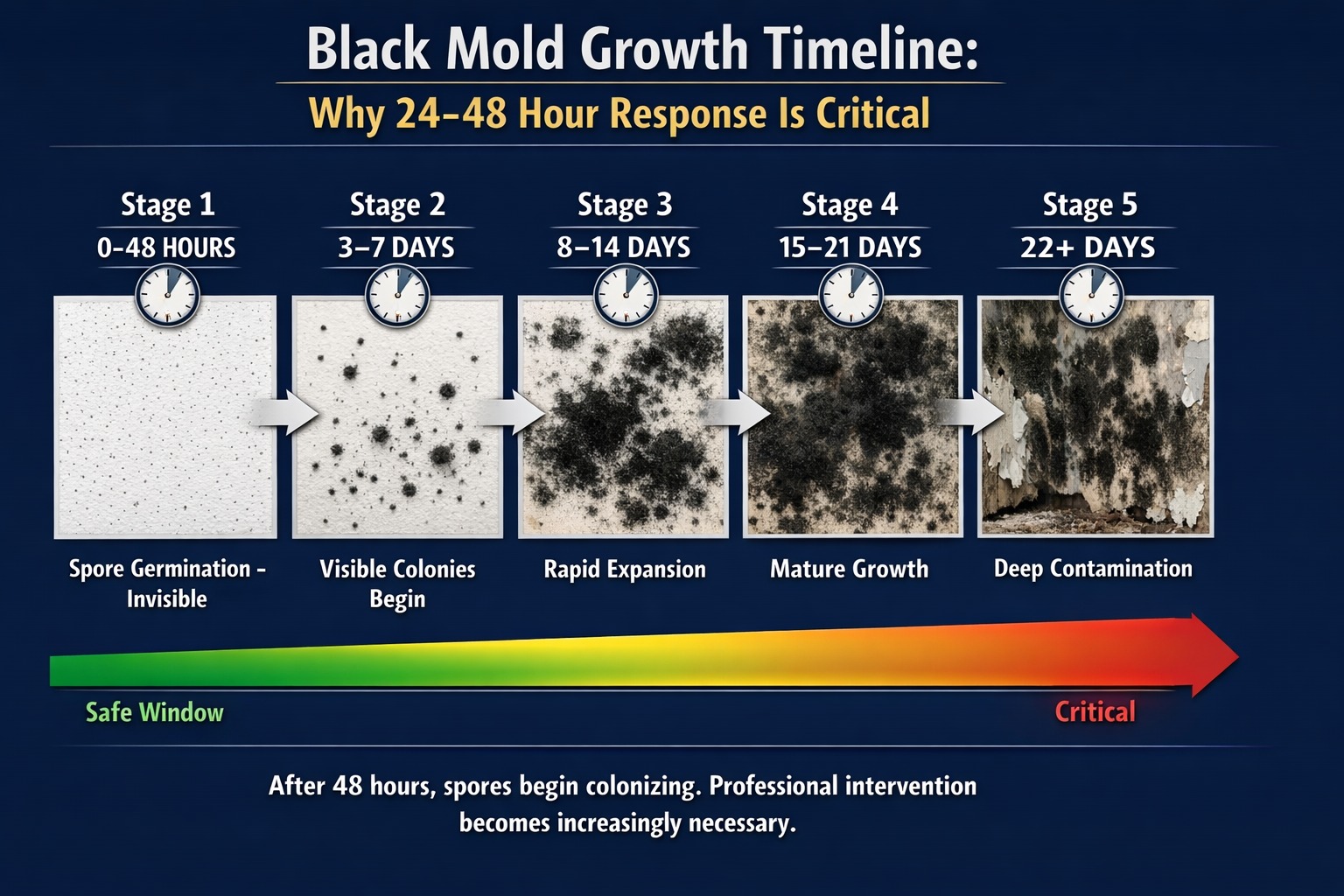
Black mold begins growing within 24 to 48 hours after spores land on damp materials. Once established, colonies expand at approximately one square inch per day under optimal conditions (70-80°F, 60%+ humidity). Within one to two weeks, a small water stain can develop into several square feet of contamination.
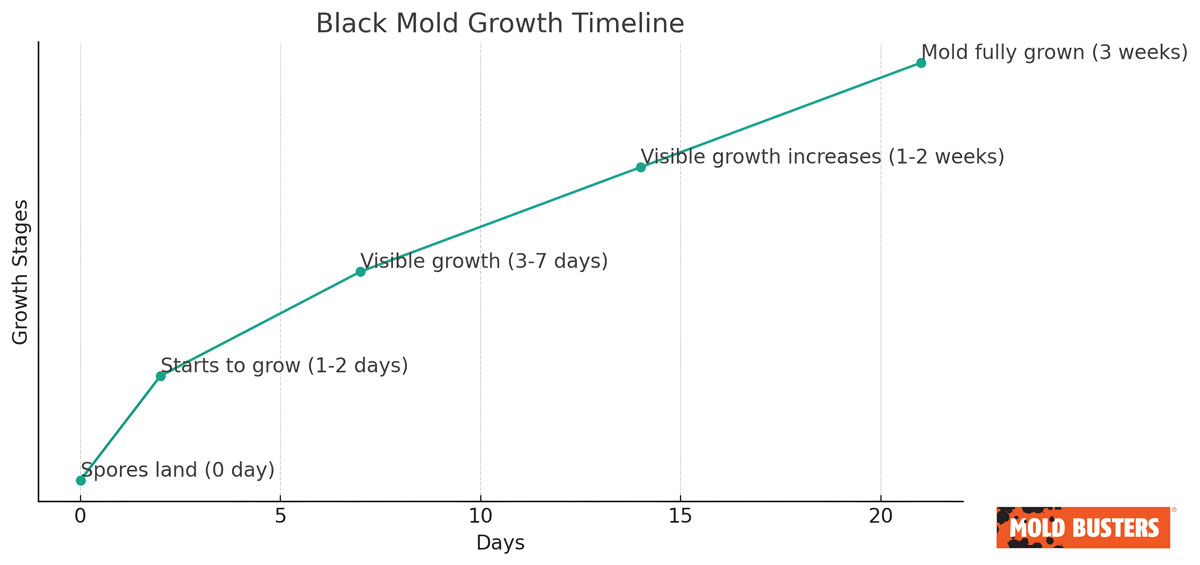
📅 Black Mold Growth Timeline
- Days 1-2: Spores germinate (microscopic, invisible)
- Days 3-7: Visible black spots appear, mycelium establishes beneath surface
- Days 8-21: Rapid expansion phase, mycotoxin production increases
- Week 4+: Mature colonies covering extensive areas, materials require removal rather than cleaning
How Fast Does Mold Grow on Walls?
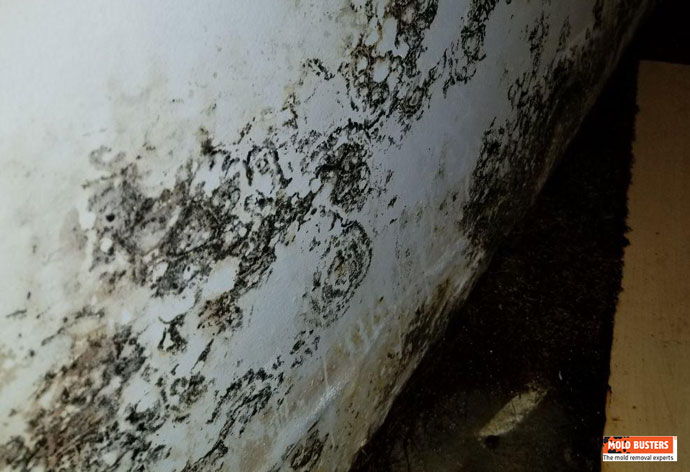

Black mold spreads particularly rapidly on drywall because it contains cellulose. On interior walls, black mold can spread from a small water stain to covering 10-15 square feet within two weeks. The mold follows moisture paths within wall cavities, often spreading faster than visible surface growth suggests.
Where Else Does Black Mold Grow?
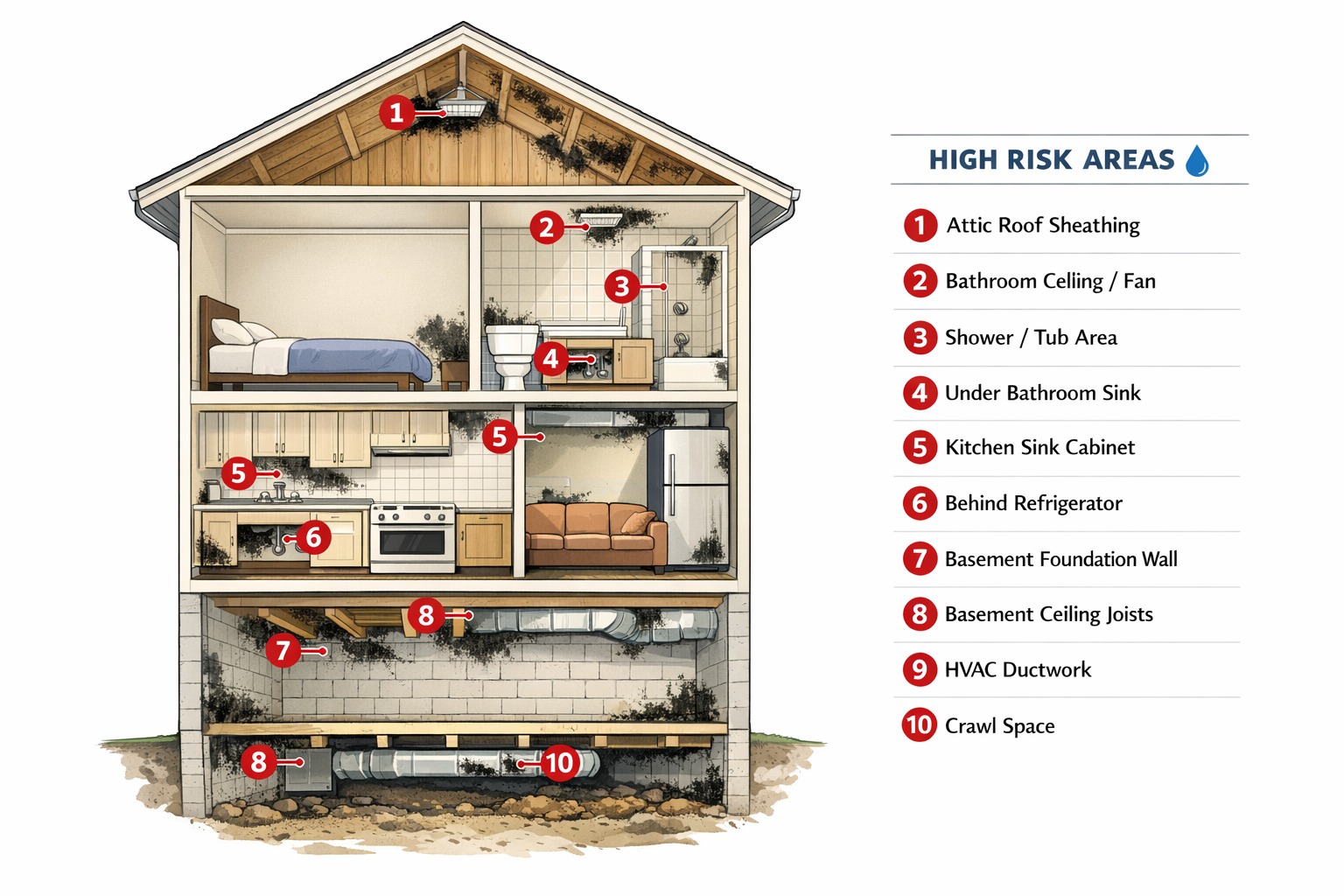
Common locations include ceiling tiles beneath leaks, wooden floor joists in damp basements, insulation materials, cardboard boxes, wallpaper backing, carpet padding, and fabric upholstery. Attics frequently develop black mold on rafters. HVAC systems can harbor extensive growth when condensation accumulates.
What Causes Black Mold to Form in Your Home?
Black mold formation requires moisture, organic material, and time. The primary trigger is water intrusion from flooding, pipe bursts, roof leaks, or chronic condensation. When moisture persists on cellulose materials for 24-48 hours, black mold spores begin colonizing.
Water damage from plumbing failures ranks as the leading cause. Leaking pipes within walls, failed supply lines, overflowing toilets, and broken water heaters can go undetected while continuously feeding moisture to materials. Inadequate ventilation transforms routine activities into breeding grounds—bathroom showers without exhaust fans, kitchens lacking range hoods, and laundry rooms with improper dryer venting release massive moisture daily.
Can Black Mold Spores Travel in the Air?
Yes. Mold spores are airborne and attach to people’s skin, clothing, shoes, furniture, carpets, and pets. Once spores enter your home, they settle onto any surface and multiply. They also enter through open doors, windows, and HVAC systems.
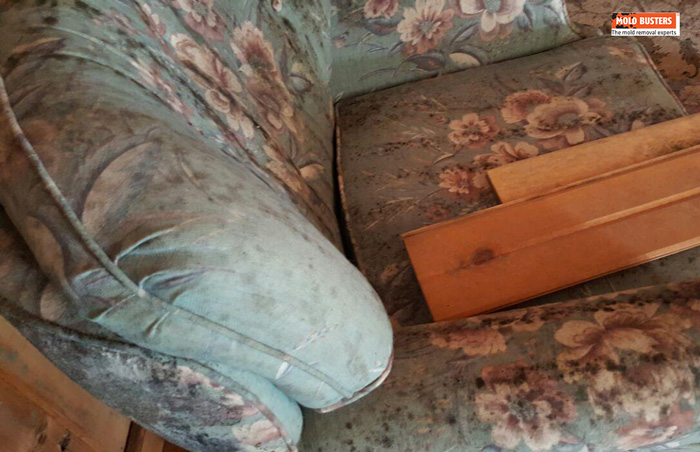

What Temperature Does Black Mold Grow Best?

🌡️ Optimal Growth Conditions
Mold thrives in warm, humid conditions. Temperatures around 70°F (20°C) are ideal for growth. However, black mold can grow in winter’s cold, wet conditions, especially near standing water.
Black Mold Health Symptoms: What Are the Risks?

Black mold exposure triggers a wide range of health symptoms varying in severity based on exposure duration, mycotoxin concentration, and individual sensitivity. The mycotoxins attack multiple body systems, suppressing immune function while triggering inflammatory responses.
🫁 Respiratory Symptoms
- Persistent coughing and wheezing
- Difficulty breathing and chest tightness
- Chronic sinus congestion and nosebleeds
- Persistent sore throat
🧠 Neurological Symptoms
- Chronic headaches and dizziness
- Difficulty concentrating and “brain fog”
- Memory problems
- Mood changes including depression and anxiety
💪 Physical Symptoms
- Extreme fatigue
- Frequent infections and slow healing
- Persistent skin rashes
- Joint and muscle pain
- Chronic eye irritation
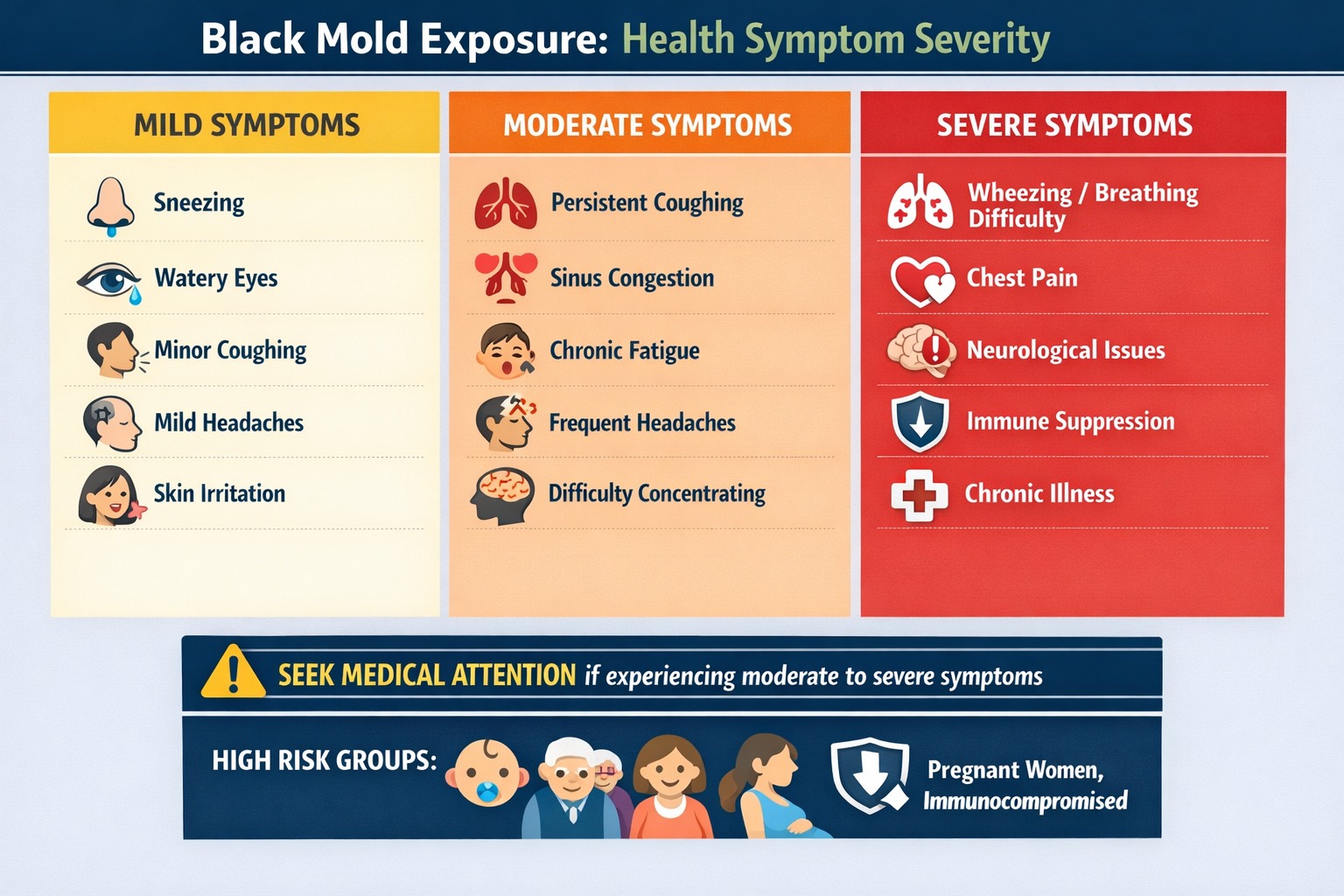
Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions experience dramatically worsened symptoms. Asthma sufferers report increased attack frequency. People with COPD find their lung function declining more rapidly than expected.
Treating Black Mold Exposure

Treatment requires eliminating ongoing exposure through professional remediation and addressing symptoms through medical intervention.
🏥 Treatment Steps
- Immediate steps: Leave the contaminated environment, seek medical evaluation, and schedule professional mold inspection
- Medical treatments: Nasal saline rinses, prescription sprays, bronchodilator inhalers, antihistamines, and in severe cases, immunotherapy
Important: No medical treatment can substitute for eliminating the black mold source.
How to Identify Black Mold in Your House
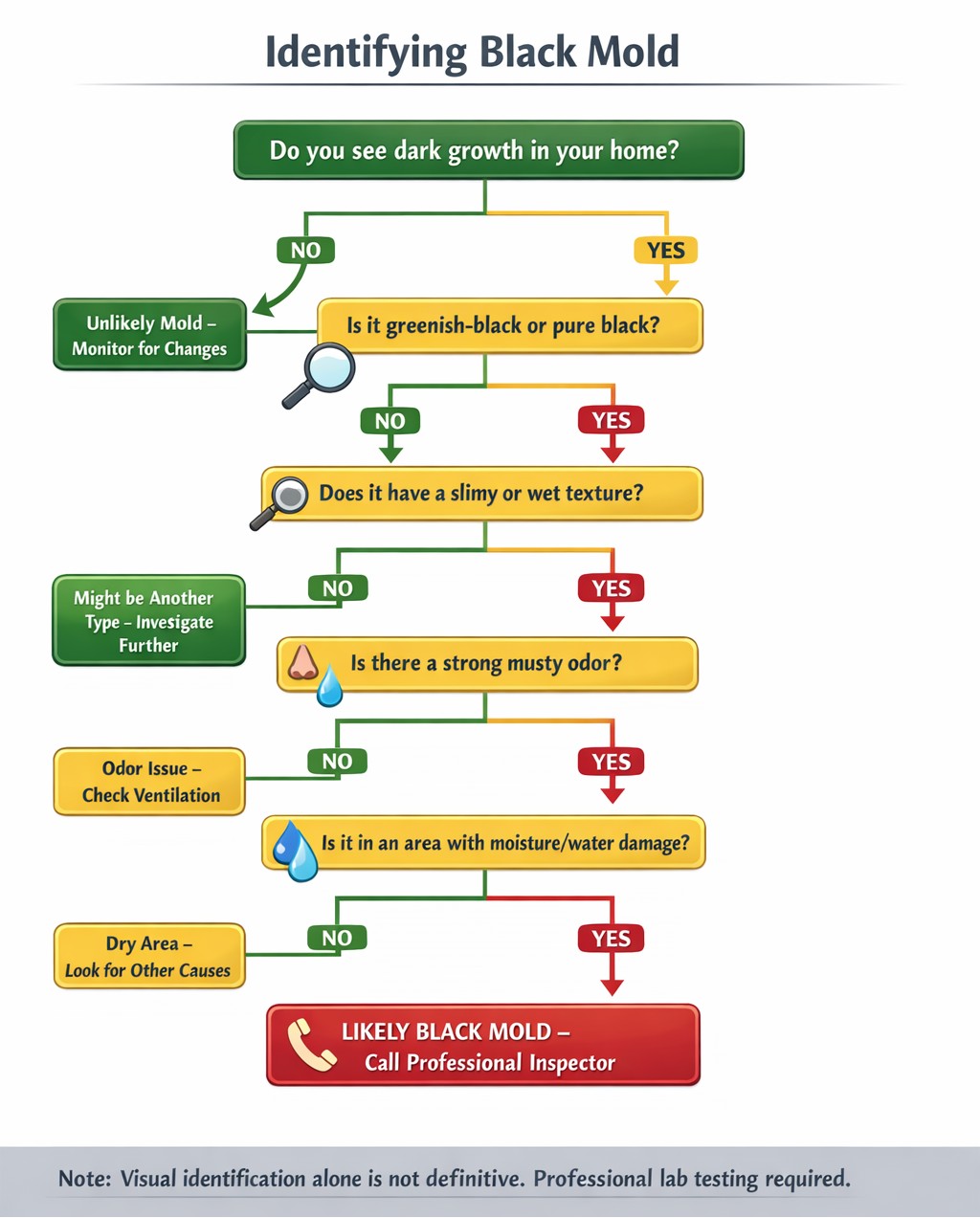
Identifying black mold requires looking beyond visual appearance since mold often grows in hidden areas. Successful identification combines visual inspection, smell detection, moisture assessment, and understanding common locations.
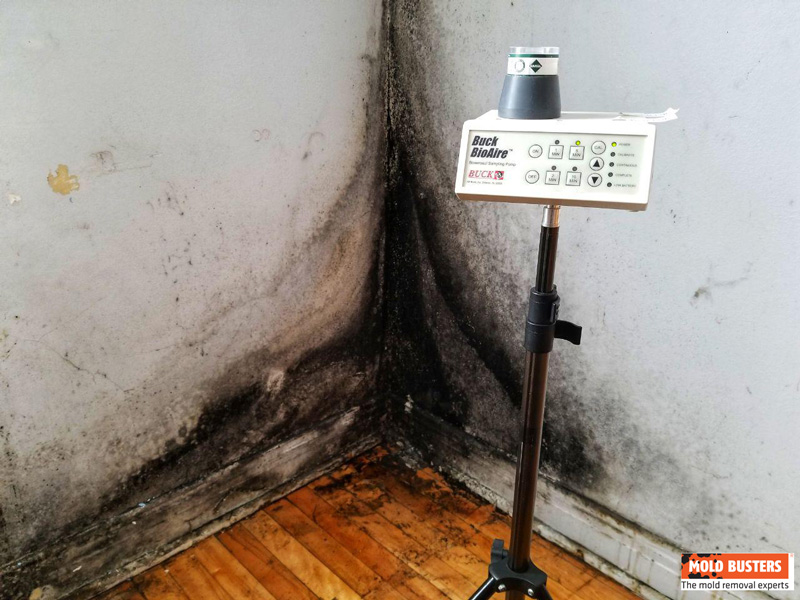

Signs of Black Mold
👁️ Visual Signs
- Dark greenish-black patches with slimy or wet texture
- Irregular spreading patterns following moisture paths
- Water stains and discoloration
- Bubbling or peeling paint
- Warped drywall
📍 Where to Check
- Behind appliances
- Under sinks
- Around toilets
- Carpet edges
- Attic insulation
Common Locations in Canadian Homes
🚿 Bathrooms
- Around showers and tubs
- Under sinks
- Behind toilets
- On ceilings without ventilation
🏠 Basements
- Foundation walls
- Around bathrooms and laundry
- Wooden joists
- Behind stored items
🏚️ Attics
- Roof sheathing near leaks
- Rafters
- Wet insulation
- Around improperly ventilated exhaust fans
🛋️ Living Areas
- Behind furniture against cold walls
- Around windows with condensation
- Closets against exterior walls
DIY vs. Professional Testing
🏪 Home Test Kits ($20-$50 + lab fees)
Can confirm mold presence but have significant limitations:
- Homeowners often miss critical areas
- They don’t identify moisture sources
- High false-negative rates occur
- Don’t provide actionable remediation plans
🔬 Professional Testing ($300-$650)
Provides comprehensive assessment:
- Accurate species identification
- Contamination extent mapping
- Moisture source analysis
- Detailed remediation recommendations
- Visual inspection with thermal imaging
- Laboratory analysis by accredited labs
💡 Tip: Mold Busters offers free virtual inspection for preliminary assessment.
How to Prevent Black Mold Growth in Your Home
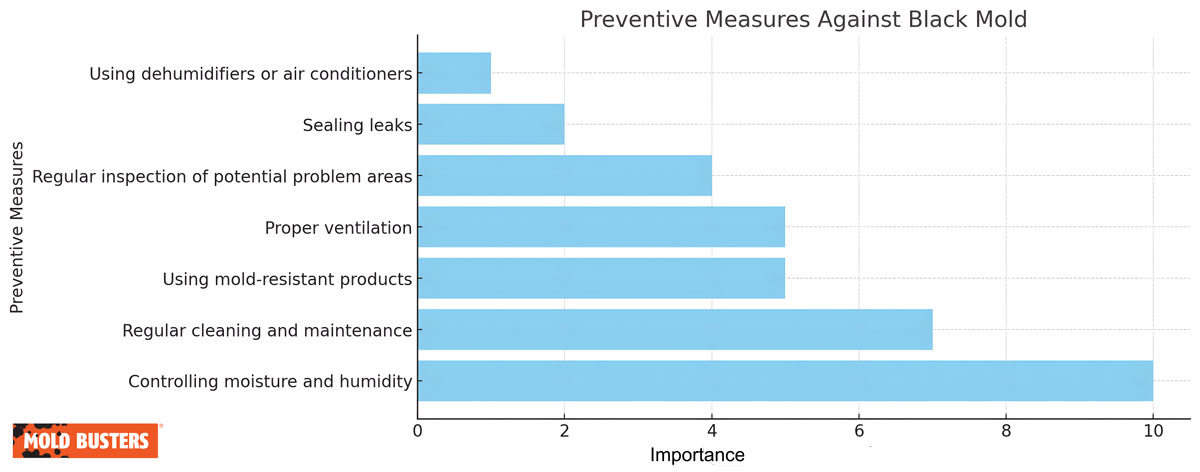
Prevention focuses on moisture control, proper ventilation, and rapid response to water problems.

💧 Key Prevention Strategies
- Control humidity below 50% using dehumidifiers
- Ensure bathroom exhaust fans vent outside and run for 30 minutes after showers
- Use kitchen range hoods venting to exterior
- Maintain proper dryer venting
- Respond rapidly to water damage within 24-48 hours
- Fix all leaks immediately rather than using temporary solutions
🍁 Seasonal Tips for Ontario & Quebec
- Winter: Monitor for ice dams
- Spring: Inspect for snowmelt seepage
- Summer: Use dehumidifiers during humid weather
- Fall: Seal foundation cracks before ground freeze
Remember: Conduct regular inspections checking for water stains, moisture, odors, and early-stage growth. Prevention is significantly less expensive than remediation.
How to Get Rid of Black Mold: Professional Removal & Cost

Black mold removal requires professional remediation due to serious health risks. Attempting DIY removal is dangerous—disturbing colonies without proper containment releases millions of toxic spores, worsening contamination.

🛠️ Professional Remediation Process
Professional companies like Mold Busters use specialized equipment and protocols:
- Comprehensive assessment with thermal imaging and testing
- Containment with negative air pressure and HEPA filtration
- Safe removal with proper disposal
- HEPA vacuuming and antimicrobial treatments
- Moisture source correction
- Post-remediation verification testing
Black Mold Removal Cost Guide (2026)
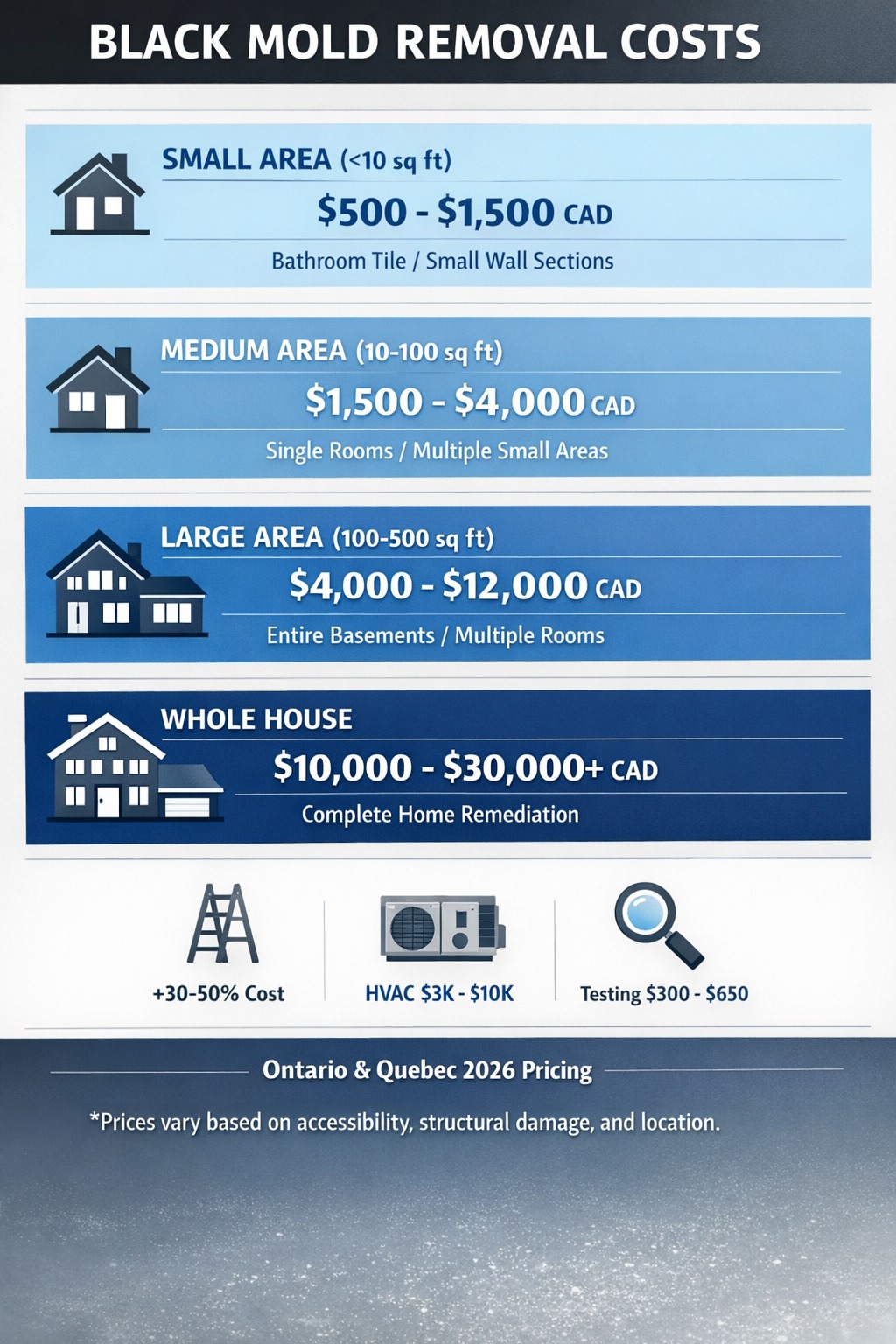
Costs vary based on contamination extent, location accessibility, and structural damage severity:
Small growth in accessible areas like bathroom walls or small basement sections.
Single rooms or multiple small areas requiring professional containment. Covers bathroom problems, bedroom walls, and small basement sections.
Entire basements, multiple rooms, or significant structural components. Requires comprehensive remediation with full containment.
Complete home contamination from major flooding or long-term leaks.
Key Cost Factors
📍 Location Accessibility
Mold behind walls, in crawl spaces, or above ceilings costs 30-50% more.
❄️ HVAC Contamination
System cleaning costs $3,000-$10,000.
🔨 Structural Repairs
- Drywall replacement: $1.50-$3.50/sq ft
- Carpet replacement: $2-$8/sq ft
- Insulation replacement: $1-$4.50/sq ft
🔬 Testing
- Initial inspection: $300-$650
- Post-remediation clearance testing: $200-$400
Does Insurance Cover Black Mold Removal?
✅ Typically Covered
- Sudden accidents like burst pipes
- Appliance failures
- Storm damage
❌ Typically Excluded
- Gradual damage from long-term leaks
- Deferred maintenance
- Chronic moisture
- External flooding (requires separate flood insurance)
Tip: Contact your insurance provider immediately upon discovering black mold. Mold Busters works directly with insurance adjusters to ensure proper documentation and maximize coverage.
Why Choose Professional Remediation
The EPA and Health Canada recommend professional remediation for contamination exceeding 10 square feet. However, even smaller black mold growth warrants professional attention for:
- Health protection during removal process
- Complete removal including hidden areas
- Preventing cross-contamination to other areas
- Warranty and guarantees on work performed
- Insurance documentation requirements
⚠️ Avoid unlicensed contractors—failed remediation requiring re-work costs significantly more than hiring qualified contractors initially.
Protecting Your Family from Black Mold Starts Now
Black mold represents a serious threat to your family’s health and your property’s structural integrity, but prompt professional intervention provides complete resolution. Whether you’ve discovered visible growth, detected suspicious odors, or experienced unexplained health symptoms, immediate action prevents the problem from worsening.
Mold Busters has served Ontario and Quebec homeowners since 2005, completing over 15,000 inspections and 5,000 remediation projects. Our IICRC-certified technicians use advanced diagnostic equipment, proper containment protocols, and EPA-registered treatments to eliminate black mold safely and completely.
✅ IICRC Certified
Industry-certified technicians with advanced training
🔬 Advanced Technology
Thermal imaging and laboratory testing
🛡️ EPA-Registered
Safe, effective treatment protocols
📞 24/7 Emergency
Rapid response when you need it most
🔧 Our Services
⚡ Why Mold Busters
- Immediate response & same-day reports
- Guaranteed results
- Insurance documentation assistance

Get Special Gift: Industry-Standard Mold Removal Guidelines
Download the industry-standard guidelines that Mold Busters use in their own mold removal services, including news, tips and special offers:
"*" indicates required fields
Published: November 23, 2018 Updated: January 12, 2026

Written by:
John Ward
Account Executive
Mold Busters
Fact checked by:
Michael Golubev
CEO
Mold Busters
